Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Fiber Optic Splice Closure: A Crucial Component in Modern Telecommunications

Fiber Optic Splice Closure: A Crucial Component in Modern Telecommunications
In the ever-evolving landscape of telecommunications, the role of fiber optics cannot be overstated. With their unparalleled speed, bandwidth, and resilience, fiber optic cables have revolutionized the way we communicate, transmit data, and connect globally. Among the various components that ensure the seamless operation of fiber optic networks, the fiber optic splice closure stands out as a vital element, tasked with both connecting and protecting these delicate cables.
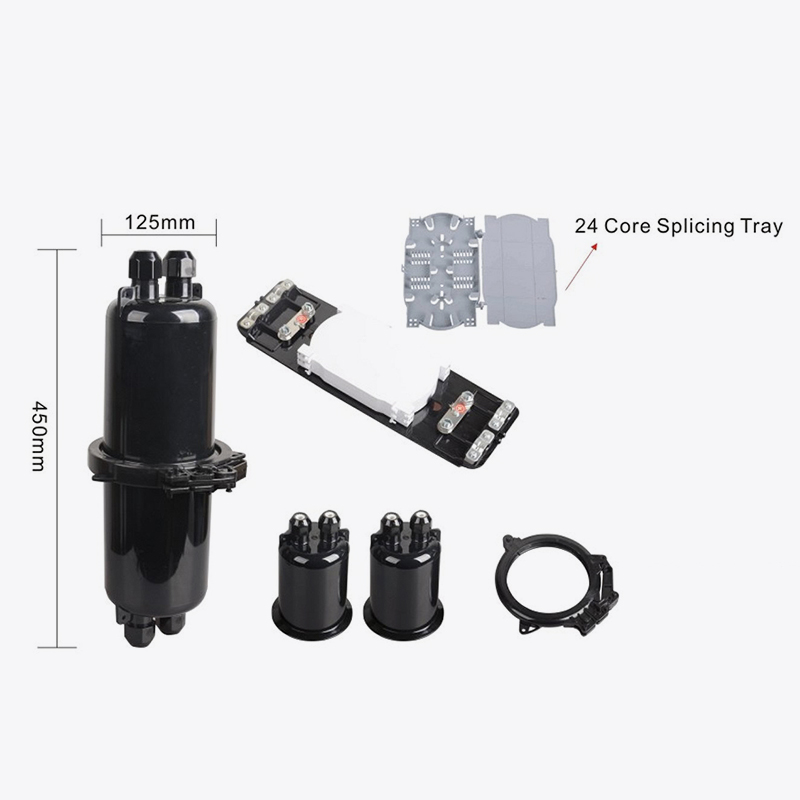
A fiber optic splice closure, is primarily used to connect and splice together optical fibers, while simultaneously providing robust protection to these connections. It serves as a crucial junction point where multiple fiber optic cables can be joined, whether they are overhead, within conduits, or buried underground. This versatility makes it indispensable in diverse environments and applications, ranging from urban cityscapes to rural landscapes.
The structure of a fiber optic splice closure is thoughtfully designed to meet rigorous standards of durability and functionality. The box body and base are typically sealed using hoops and rubber, creating a watertight and dustproof environment that safeguards the sensitive optical fibers from environmental threats such as moisture, dirt, and extreme temperatures. This sealing mechanism is crucial, as any contamination or exposure to harsh conditions can degrade fiber performance or lead to network failures.
The closure casing itself is usually crafted from high-quality engineering plastics, chosen for their exceptional resistance to erosion from acid, alkali salt, and other腐蚀性物质. This material not only ensures a long service life but also contributes to the closure's overall robustness and reliability. Furthermore, the plastic casing offers a smooth appearance, which facilitates easier handling and installation.
Beneath its sturdy exterior, the fiber optic splice closure houses an intricate mechanical structure that is designed to withstand the most challenging conditions. This structure must be able to resist the rigors of wild environments, where climate changes can be intense and working conditions demanding. From scorching desert heat to icy mountain cold, the splice closure must remain intact and operational, ensuring uninterrupted service.
Inside the closure, splice trays (FOST) play a pivotal role. These trays are designed to be turnable, akin to booklets, allowing technicians easy access to the spliced fibers. They feature an adequate curvature radius and sufficient space for winding the optical fibers, ensuring that the minimum bending radius for optical winding—typically 40 mm—is maintained. This is crucial, as excessive bending can cause signal loss or even damage to the fibers.
Another notable feature of fiber optic splice closures is their modular design, which allows for individual operation of each optical cable and fiber. This means that maintenance or repairs can be carried out without disrupting the entire network, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency.
Reusability and Environmental Impact
An additional advantage of fiber optic splice closures is their reusability. Unlike some other components in the telecommunications industry, splice closures can be opened and reused after installation, reducing waste and promoting sustainability. This is particularly important in an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, and reducing the carbon footprint of technology is a collective goal.
 Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China
Address:Zhong'an Road, Puzhuang Town, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Prov., China Phone:+86-189 1350 1815
Phone:+86-189 1350 1815 Tel:+86-512-66392923
Tel:+86-512-66392923 Fax:+86-512-66383830
Fax:+86-512-66383830 Email:[email protected]
Email:[email protected] Wechat: xiaobin18913501815
Wechat: xiaobin18913501815 whatsapp: +86 18913501815
whatsapp: +86 18913501815
 0
0

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى